Plant respiration is a fundamental process that is essential for plant life. Much like animals, plants undergo respiration to break down sugars and release energy for their metabolic activities. While plants are known for photosynthesis, where they produce oxygen, respiration is equally important because it provides the energy needed for growth, maintenance, and survival. Understanding plant respiration will give you a clearer picture of how plants function and thrive, day and night.
What Is Plant Respiration?
Plant respiration is a metabolic process in which plants convert sugars (produced during photosynthesis) and oxygen into energy, carbon dioxide, and water. This energy is used to power the various processes necessary for plant growth and development. Unlike photosynthesis, which only occurs in the presence of light, respiration happens continuously—both during the day and at night.
The Basic Equation for Plant Respiration
The chemical equation for plant respiration is:
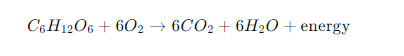
This equation represents the breakdown of glucose (sugar) in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy (in the form of ATP).
- Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆): The main sugar produced during photosynthesis, used as the fuel for respiration.
- Oxygen (O₂): Absorbed by plants from the atmosphere, crucial for breaking down sugars.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): Released as a by-product of respiration and expelled through the plant’s stomata.
- Water (H₂O): Produced during respiration and either used by the plant or released through transpiration.
- Energy (ATP): The main product of respiration, providing energy for cellular functions.
How Does Plant Respiration Work?
Plant respiration takes place at the cellular level, specifically within the mitochondria of plant cells. Mitochondria are often called the “powerhouses” of the cell because they generate the energy that plants need to carry out various functions. Here’s a breakdown of the respiration process:
1. Glycolysis
The first step of respiration is glycolysis, which occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into pyruvate, producing a small amount of energy (ATP) and releasing electrons. This process does not require oxygen and is the initial phase of energy production.
2. Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
After glycolysis, pyruvate enters the mitochondria, where it undergoes the Krebs cycle. This process generates carbon dioxide, energy-rich molecules (NADH and FADH₂), and a small amount of ATP. The Krebs cycle is an aerobic process, meaning it requires oxygen.
3. Electron Transport Chain
The final stage of respiration occurs in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. Electrons from NADH and FADH₂ are passed along the electron transport chain, releasing energy that is used to produce ATP. At the end of the chain, oxygen combines with electrons and hydrogen ions to form water. This stage produces the majority of the ATP that plants need.
4. Release of Carbon Dioxide and Water
As a by-product of respiration, plants release carbon dioxide and water. Carbon dioxide exits the plant through tiny pores called stomata, which are primarily located on the undersides of leaves. Water produced during respiration can either be used by the plant for other processes or released into the atmosphere through transpiration.
The Role of Stomata in Respiration
Stomata play a critical role in plant respiration, as they are responsible for the exchange of gases between the plant and its environment. These small openings on the leaves allow oxygen to enter the plant during respiration and enable the release of carbon dioxide as a by-product.
Daytime vs. Nighttime Respiration
During the day, plants are busy with photosynthesis, where they absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen. However, at night, when photosynthesis stops, respiration continues. At night, plants absorb oxygen from the atmosphere through the stomata and release carbon dioxide, the opposite of what happens during the day.
- Daytime: Photosynthesis dominates, with oxygen being released and carbon dioxide absorbed.
- Nighttime: Respiration takes over, with oxygen absorbed and carbon dioxide released.
Importance of Plant Respiration
Respiration is essential for plants because it provides the energy they need to grow, repair tissues, and carry out vital functions. Without respiration, plants would be unable to convert the sugars produced during photosynthesis into usable energy.
1. Energy Production
The primary purpose of respiration is to produce ATP, the energy currency of cells. This energy powers processes such as nutrient uptake, cell division, and protein synthesis, all of which are essential for plant growth.
2. Growth and Development
Respiration supplies the energy needed for plants to grow and develop. Whether it’s forming new leaves, flowers, or roots, energy from respiration drives these activities.
3. Maintenance and Repair
Plants constantly repair damaged tissues and maintain their cellular structures. Respiration provides the energy needed for these maintenance processes, ensuring that plants stay healthy and functional.
4. Stress Response
When plants face environmental stresses such as drought, extreme temperatures, or pest attacks, respiration helps them cope. By providing energy, respiration supports the plant’s ability to respond and adapt to challenging conditions.
Factors Affecting Plant Respiration
Several environmental factors can influence the rate of plant respiration. Understanding these factors can help you create optimal growing conditions for your plants.
1. Temperature
Respiration rates increase with temperature because warmer temperatures accelerate metabolic processes. However, excessively high temperatures can lead to faster respiration rates, causing the plant to use up its energy reserves quickly, which can result in stress. Conversely, low temperatures can slow down respiration, reducing energy production.
2. Oxygen Availability
Oxygen is essential for respiration, so plants grown in poorly aerated soils or waterlogged conditions may experience reduced respiration rates. Without adequate oxygen, plants struggle to break down sugars efficiently, leading to poor growth.
3. Light
While light itself doesn’t directly affect respiration, it influences the rate of photosynthesis, which in turn affects the availability of sugars for respiration. During periods of high light intensity, plants produce more glucose through photosynthesis, which provides more fuel for respiration.
4. Water Availability
Water is crucial for respiration, as it helps transport nutrients and oxygen within the plant. In drought conditions, plants may reduce their respiration rate to conserve water and energy. Conversely, overwatering can lead to root rot, which impairs respiration by limiting oxygen availability to the roots.
Balancing Photosynthesis and Respiration
Photosynthesis and respiration are interconnected processes that together sustain plant life. While photosynthesis is responsible for producing the sugars that fuel growth, respiration breaks down these sugars to release energy. A balance between these two processes is vital for plant health.
- Photosynthesis: Occurs in the chloroplasts and produces glucose and oxygen using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water.
- Respiration: Occurs in the mitochondria and breaks down glucose to release energy, water, and carbon dioxide.
Plants need both processes to function properly. Photosynthesis provides the food, while respiration converts that food into energy for growth and maintenance.
Conclusion
Plant respiration is a critical process that ensures plants have the energy they need to grow, maintain themselves, and respond to environmental challenges. Understanding the basics of plant respiration, including how it differs from photosynthesis and the factors that affect it, can help you provide better care for your plants. By creating optimal conditions for respiration, you can promote healthier, more vigorous plants in your garden.
FAQs
Do plants breathe like humans?
Plants don’t breathe in the same way humans do, but they do take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide during respiration. This process occurs at the cellular level and is necessary for producing energy.
How is plant respiration different from photosynthesis?
Respiration is the process of breaking down sugars to release energy, while photosynthesis is the process of using sunlight to produce sugars. Photosynthesis occurs in the presence of light, while respiration happens continuously.
Does plant respiration only happen at night?
No, plant respiration occurs both day and night. However, it is more noticeable at night because photosynthesis (which produces oxygen) stops, and the plant relies solely on respiration to break down sugars and release carbon dioxide.
Can respiration harm plants?
While respiration is essential for plant survival, if environmental conditions cause respiration rates to exceed photosynthesis, plants may deplete their energy reserves. This can happen in extremely hot conditions or when oxygen levels are too low.
How can I ensure healthy respiration in my plants?
To promote healthy respiration, ensure your plants have well-draining soil, adequate oxygen around the roots, and optimal temperature conditions. Avoid overwatering, and make sure plants have access to the nutrients they need for energy production.



